Anatomy and Physiology of Lymphatic System
There are seven main body systems
- Muscular System
- Skeletal system
- Nervous System
- Digestive System
- Respiratory system
- Excretory system
- Circulatory system
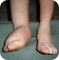
The lymphatic system aids the immune system by removing and destroying toxins, bacteria, germs, cancer cells and waste.
When the lymphatic system is at risk of not functioning properly, due to chronic medical conditions, chemotherapy, radiation and obesity all the bodies system will be affected. There are seven main body systems which all play an important role working with the Lymphatic System.
A compromised Lymphatic System will often have a holistic effect on all the body systems. The human body relies on millions of cells throughout the body to communicate and work together, allowing the systems to work at their maximum potential.
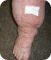
If the Excretory System was diseased and failing, this would put a heavy load on the Lymphatic System. There would be excess fluid building up around the cells, causing swelling in around the tissues.
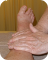
When there is limited mobility in any limb, this slows down the Muscular System from being able to pump the lymph fluid through to the vessels. Unlike blood which has the heart to pump it through the Circulatory System, the lymphatic system needs the contraction of the muscles to pump the lymph fluid through the bodies system.
A compromised Circulatory System, which initially carries the lymph fluid as plasma in the blood, will affect the Lymphatic System if there is any venous insufficiency or heart condition.
The Digestive System also plays a major part in transporting the lymph fluid through all the organs associated with the Digestive System. A sluggish fatty and congested Digestive System can slow down lymph flow, causing fluid to back up in and around the tissues causing swelling.
In many cases chronic medical conditions within the Respiratory System, also cause swelling known as Lymphoedema. In the case of lung disease, especially caused from smoking, can thicken the walls of the main arteries and veins from the lungs to the heart making it hard to breathe. Slow breathing and blood flow from blocked arteries can also cause Venous Insufficiency causing swelling of the limbs (lymphoedema).